Three mysterious facts about Antarctica that you probably didn't know
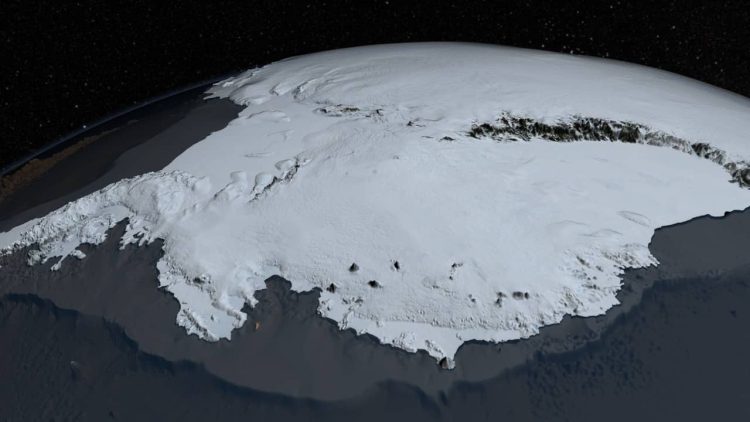
Antarctica is one of the world's most mysterious and least explored continents. This kingdom of ice and snow holds many fascinating secrets that continue to attract scientists and curious people from all over the world. Here are three mysterious facts about Antarctica that you may not have heard.
January 12, 2025 08:07
1. A huge underwater lake frozen in ice
Most of Antarctica's unique natural "monuments" lie in the lower part of glaciers. One such phenomenon is Lake Vostok, the largest lake in Antarctica. This spectacular lake swims beneath nearly 4 kilometres of ice. Scientists believe that this lake may have existed for more than 15 million years and has a unique ecosystem that scientists are still exploring.
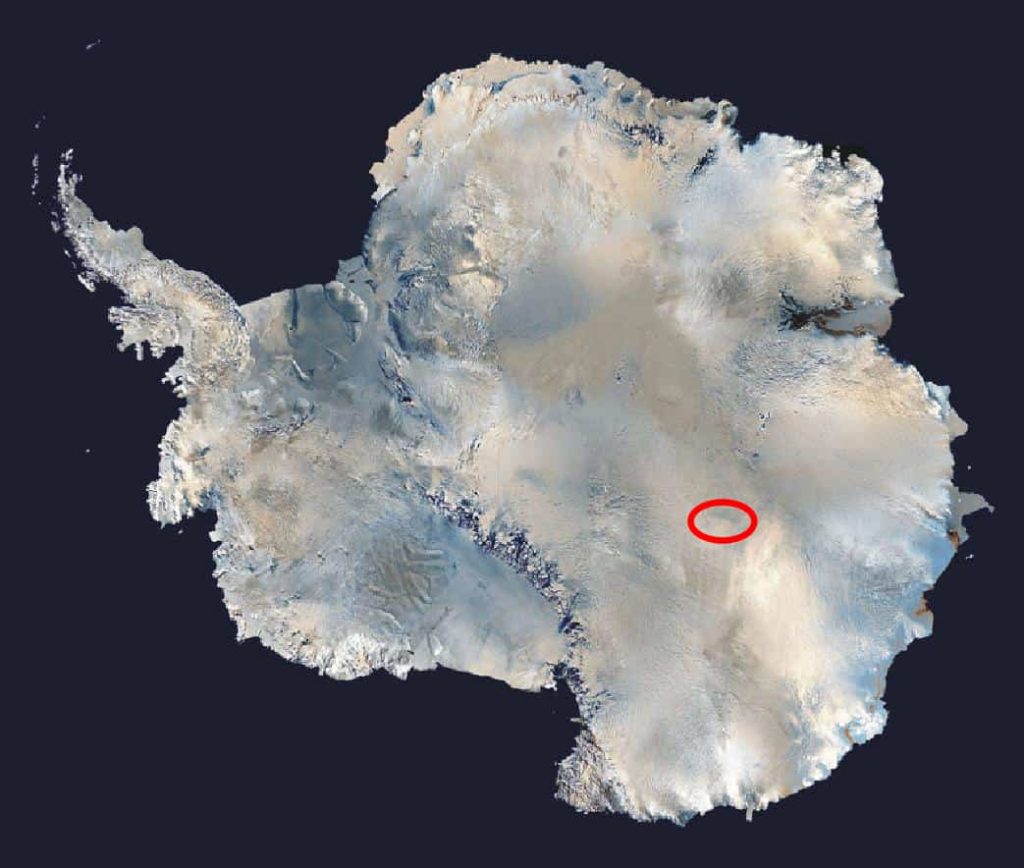

Antarctica is also home to another famous lake called Enigma. Scientists have recently discovered a layer of fresh water hidden beneath the ice, which is home to a variety of micro-organisms - a very important scientific discovery. Read more about it here.
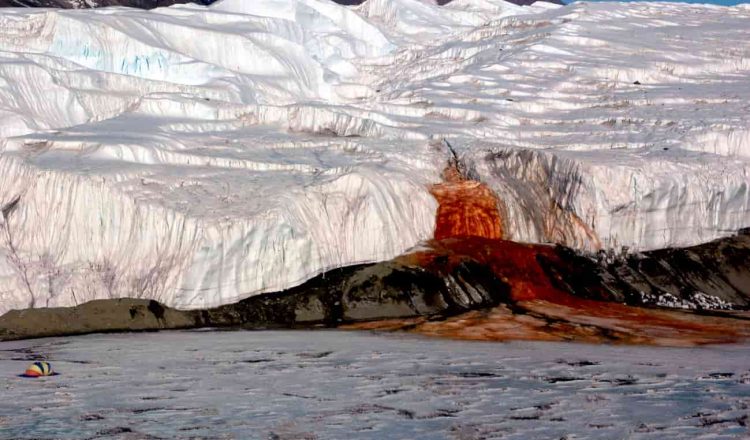
2. The mysterious "Blood Falls"
In Antarctica, near the Voronoi Glacier, there is a unique phenomenon known as "Blood Falls". These are trails of red water flowing out of the glaciers. The colour of this phenomenon is caused by the oxidation of iron as salt water melts from the subglacial lakes and interacts with oxygen. This mysterious phenomenon gives researchers the opportunity to study life forms that are able to exist in extreme conditions.

3. The thickness of the Antarctic ice reaches up to 4.8 kilometersThe Antarctic ice is impressively thick, reaching up to 4.8 kilometers in places. This gigantic ice sheet has been accumulating for millions of years. Thick ice covers various parts of the continent, but is especially concentrated in the eastern part of Antarctica.
The importance of this ice mass to the world is enormous, as it holds frozen about 60% of the world's fresh water reserves. If all of this ice were to melt, global ocean levels could rise by about 58 meters, which would have enormous effects on global geography and climate.
The great thickness of the ice also makes Antarctica a valuable research site for climatologists and geologists seeking to understand past climate variability and predict future climate change. Ice cores store information on ancient atmospheric gases, allowing scientists to reconstruct climate history going back many millennia.





